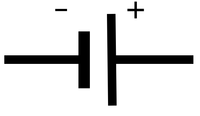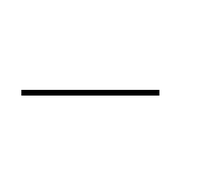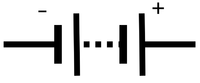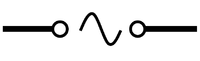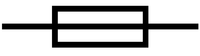Difference between revisions of "Electrical Component"
(→Key Stage 3) |
(→Examples) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 133: | Line 133: | ||
: The '''components''' you should know are: | : The '''components''' you should know are: | ||
*[[Electrical Cell]] | *[[Electrical Cell]] | ||
| + | *[[Battery]] | ||
| + | *[[Variable Power Supply]] | ||
| + | *[[Alternating Current Supply]] | ||
*[[Wire]]s | *[[Wire]]s | ||
*[[Electrical Bulb]] | *[[Electrical Bulb]] | ||
| Line 141: | Line 144: | ||
*[[Voltmeter]] | *[[Voltmeter]] | ||
*[[Ammeter]] | *[[Ammeter]] | ||
| + | *[[Variable Resistor]] | ||
| + | *[[Light Dependent Resistor]] | ||
| + | *[[Thermistor]] | ||
| + | *[[Diode]] | ||
| + | *[[Light Emitting Diode]] | ||
| + | *[[Electrical Fuse]] | ||
===Examples=== | ===Examples=== | ||
| Line 146: | Line 155: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Electrical Cell''' | |'''Electrical Cell''' | ||
| + | |'''Battery''' | ||
| + | |'''Variable Power Supply''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:CellSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:BatterySymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:VariablePowerSupplySymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[Electrical Cell|cell]] makes the [[electricity]] flow in a [[circuit]]. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[battery]] is several [[Electrical Cell|cells]] connected together. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[Variable Power Supply|variable power supply]] is a source of [[electricity]] with a [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] which can be changed. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |'''Alternating Current Supply''' | ||
|'''Wires''' | |'''Wires''' | ||
|'''Filament Bulb''' | |'''Filament Bulb''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[File: | + | |[[File:AlternatingCurrentSupplySymbol.png|center|200px]] |
|[[File:WireSymbol.png|center|200px]] | |[[File:WireSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
|[[File:BulbSymbol.png|center|200px]] | |[[File:BulbSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" | | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |An [[Alternating Current Supply|alternating current supply]] is a source of [[electricity]] with an [[Alternating Current|alternating current]]. |
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" | | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Wire]]s are the path for [[electricity]] to flow. |
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A filament bulb lights up when electricity flows through it. | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[Electrical Bulb|filament bulb]] lights up when [[electricity]] flows through it. |
|} | |} | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 167: | Line 190: | ||
|[[File:MotorSymbol.png|center|200px]] | |[[File:MotorSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
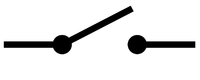
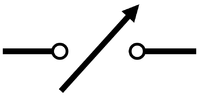
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A switch can complete or break a circuit to turn it on and off. | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[Electrical Switch|switch]] can complete or break a [[circuit]] to turn it on and off. |
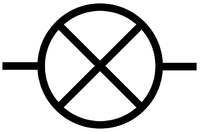
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A buzzer makes a sound when electricity flows through it. | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[buzzer]] makes a [[sound]] when [[electricity]] flows through it. |
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A motor spins when electricity flows through it. | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[motor]] spins when [[electricity]] flows through it. |
|} | |} | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 185: | Line 208: | ||
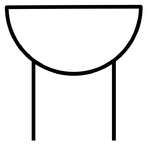
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |An [[Ammeter]] is used to [[measure]] the [[Electrical Current|Current]] passing through part of a [[circuit]]. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |An [[Ammeter]] is used to [[measure]] the [[Electrical Current|Current]] passing through part of a [[circuit]]. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
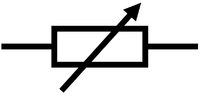
|'''Variable Resistor''' | |'''Variable Resistor''' | ||
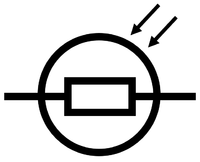
|'''Light Dependent Resistor''' | |'''Light Dependent Resistor''' | ||
| Line 196: | Line 221: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[Light Dependent Resistor|light dependent resistor (LDR)]] changes [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] depending on [[light]] intensity, the lower the intensity the greater the [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]]. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[Light Dependent Resistor|light dependent resistor (LDR)]] changes [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] depending on [[light]] intensity, the lower the intensity the greater the [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]]. | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[thermistor]] changes [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] depending on the [[temperature]]. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[thermistor]] changes [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] depending on the [[temperature]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |'''Diode''' | ||
| + | |'''Light Emitting Diode''' | ||
| + | |'''Fuse''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:DiodeSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:LightEmittingDiodeSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:FuseSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diode]] only allows [[Electrical Current|current]] through in one direction. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[Light Emitting Diode|light emitting diode (LED)]] only allows [[Electrical Current|current]] through in one direction and produces light when a [[Electrical Current|current]] passes through it. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[Electrical Fuse|fuse]] is a thin piece of [[wire]] that will [[melt]] if too much [[Electrical Current|current]] passes through it. | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 12:08, 26 February 2019
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
A component is a part of an electrical circuit.
About Components
- Components in a circuit are used to do different jobs.
- The components you should know are:
Examples
| Electrical Cell | Wires | Filament Bulb |
| A cell makes the electricity flow in a circuit. | Wires are the path for electricity to flow. | A filament bulb lights up when electricity flows through it. |
| Switch | Buzzer | Motor |
| A switch can complete or break a circuit to turn it on and off. | A buzzer makes a sound when electricity flows through it. | A motor spins when electricity flows through it. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A component is a part of an electrical circuit.
About Components
- Components in a circuit are used to do different jobs.
- The components you should know are:
Examples
| Electrical Cell | Wires | Filament Bulb |
| A cell makes the electricity flow in a circuit. | Wires are the path for electricity to flow. | A filament bulb lights up when electricity flows through it. |
| Switch | Buzzer | Motor |
| A switch can complete or break a circuit to turn it on and off. | A buzzer makes a sound when electricity flows through it. | A motor spins when electricity flows through it. |
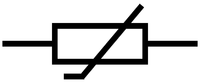
| Resistor | Voltmeter | Ammeter |
| A resistor reduces the flow of current through a circuit. | A Voltmeter is used to measure the Potential Difference between two points on a circuit. | An Ammeter is used to measure the Current passing through part of a circuit. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A component is a part of an electrical circuit.
About Components
- Components in a circuit are used to do different jobs.
- The components you should know are:
- Electrical Cell
- Battery
- Variable Power Supply
- Alternating Current Supply
- Wires
- Electrical Bulb
- Switch
- Buzzer
- Motor
- Resistor
- Voltmeter
- Ammeter
- Variable Resistor
- Light Dependent Resistor
- Thermistor
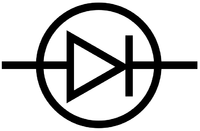
- Diode
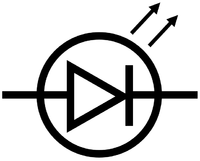
- Light Emitting Diode
- Electrical Fuse
Examples
| Electrical Cell | Battery | Variable Power Supply |
| A cell makes the electricity flow in a circuit. | A battery is several cells connected together. | A variable power supply is a source of electricity with a potential difference which can be changed. |
| Alternating Current Supply | Wires | Filament Bulb |
| An alternating current supply is a source of electricity with an alternating current. | Wires are the path for electricity to flow. | A filament bulb lights up when electricity flows through it. |
| Switch | Buzzer | Motor |
| A switch can complete or break a circuit to turn it on and off. | A buzzer makes a sound when electricity flows through it. | A motor spins when electricity flows through it. |
| Resistor | Voltmeter | Ammeter |
| A resistor reduces the flow of current through a circuit. | A Voltmeter is used to measure the Potential Difference between two points on a circuit. | An Ammeter is used to measure the Current passing through part of a circuit. |
| Variable Resistor | Light Dependent Resistor | Thermistor |
| A variable resistor can change resistance controlling the current flowing through a circuit. | A light dependent resistor (LDR) changes resistance depending on light intensity, the lower the intensity the greater the resistance. | A thermistor changes resistance depending on the temperature. |
| Diode | Light Emitting Diode | Fuse |
| A diode only allows current through in one direction. | A light emitting diode (LED) only allows current through in one direction and produces light when a current passes through it. | A fuse is a thin piece of wire that will melt if too much current passes through it. |