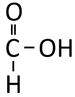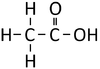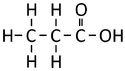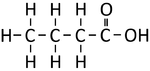Difference between revisions of "Carboxylic Acid"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 4== ===Meaning=== Carboxylic Acids are organic compounds with a Carbon atom which has a double bonds to an Oxyge...") |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | [[Carboxylic Acid]]s are [[Organic Compound|organic compounds]] with a [[Carbon]] [[atom]] which has a [[Double Bond|double bonds]] to an [[Oxygen]] [[atom]] and a [[Single Bond|single bond]] to an OH group. The [[General Formula|general formula]] is C<sub>n</sub>H<sub>2n</sub>O<sub>2</sub> | + | [[Carboxylic Acid]]s are [[Organic Compound|organic compounds]] with a [[Carbon]] [[atom]] which has a [[Double Bond|double bonds]] to an [[Oxygen]] [[atom]] and a [[Single Bond|single bond]] to an OH group. The [[General Formula|general formula]] is C<sub>n</sub>H<sub>2n</sub>O<sub>2</sub>. |
===About Carboxylic Acids=== | ===About Carboxylic Acids=== | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:75px; text-align:center;" | |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''Methanoic Acid''' |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | ===References=== |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | ====AQA==== |
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Carboxylic acids, page 183, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945571/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945571&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9e29fad914244909903e5e93f8a01d73 ''Carboxylic acids, page 82, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Carboxylic acids, pages 161, 163-165, 170-171, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Carboxylic acids, pages 242, 243, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Carboxylic acids; production from alcohols, page 182, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Carboxylic acids; properties and reactions of, page 184, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''Ethanoic Acid''' | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''Propanoic Acid''' | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''Butanoic Acid''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:75px; text-align:center;" |[[Chemical Formula]] |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |CH<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>4</sub>O<sub>2</sub> |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |C<sub>3</sub>H<sub>6</sub>O<sub>2</sub> |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>8</sub>O<sub>2</sub> |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:75px; text-align:center;" |[[Structural Formula]] |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |HCOOH |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |CH<sub>3</sub>COOH |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |CH<sub>3</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>COOH |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |CH<sub>3</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>COOH |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:75px; text-align:center;" |[[Structural Diagram]] |
| − | |[[File: | + | |[[File:StructuralDiagramMethanoicAcid.png|center|75px]] |
| − | |[[File: | + | |[[File:StructuralDiagramEthanoicAcid.png|center|100px]] |
| − | |[[File: | + | |[[File:StructuralDiagramPropanoicAcid.png|center|125px]] |
| − | |[[File: | + | |[[File:StructuralDiagramButanoicAcid.png|center|150px]] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:75px; text-align:center;" |[[Ball and Stick Model]] |
| − | |[[File: | + | |[[File:BallandStickMethanoicAcid.png|center|75px]] |
| − | |[[File: | + | |[[File:BallandStickEthanoicAcid.png|center|100px]] |
| − | |[[File: | + | |[[File:BallandStickPropanoicAcid.png|center|125px]] |
| − | |[[File: | + | |[[File:BallandStickButanoicAcid.png|center|150px]] |
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Reactions of Carboxylic Acids=== | ||
| + | ====Neutralisation==== | ||
| + | [[Carboxylic Acid]]s can be [[neutralise (Chemistry)|neutralised]] to [[Product|produce]] [[Organic Compound|organic]] [[salt]]s. | ||
| + | : [[Methanoic Acid]] + [[Potassium]] → [[Potassium Methanoate]] + [[Hydrogen]] | ||
| + | <math>2HCOOH + 2K → 2HCOOK + H_2</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Ethanoic Acid]] + [[Magnesium Oxide]] → [[Magnesium Ethanoate]] + [[Water]] | ||
| + | <math>2CH_3COOH + MgO → (CH3COO)_2Mg + H_2O</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Propanoic Acid]] + [[Sodium Hydroxide]] → [[Sodium Propanoate]] + [[Water]] | ||
| + | <math>C_2H_5COOH + NaOH → C_2H_5COONa + H_2O</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Butanoic Acid]] + [[Magnesium Carbonate]] → [[Magnesium Butanoate]] + [[Water]] + [[Carbon Dioxide]] | ||
| + | <math>2C_3H_7COOH + MgCO_3 → (C_3H_7COO)_2Mg + H_2O + CO_2</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Esterification==== | ||
| + | [[Carboxylic Acid]]s may [[Chemical Reaction|react]] with [[alcohol]]s to [[product|produce]] [[compound]]s known as [[ester]]s which have the [[Functional Group|functional group]] -COO-. | ||
| + | : [[Methanoic Acid]] + [[Ethanol]] → Ethyl Methanoate + [[Water]] | ||
| + | <math>HCOOH + C2_H_5OH → HCOOC_2H_5 + H_2O</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Ethanoic Acid]] + [[Ethanol]] → Ethyl Ethanoate + [[Water]] | ||
| + | <math>CH_3COOH + C_2H_5OH → CH_3COOC_2H_5 + H_2O</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Propanoic Acid]] + [[Propanol]] → Propyl Propanoate + [[Water]] | ||
| + | <math>C_3H_5COOH + C_3H_7OH → C_2H_5COOC_3H_7 + H_2O</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[Butanoic Acid]] + [[Propanol]] → Propyl Butanoate + [[Water]] | ||
| + | <math>C_3H_5COOH + C_3H_7OH → C_3H_5COOC_3H_7 + H_2O</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Carboxylic acids, page 183, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945571/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945571&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9e29fad914244909903e5e93f8a01d73 ''Carboxylic acids, page 82, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Carboxylic acids, pages 161, 163-165, 170-171, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Carboxylic acids, pages 242, 243, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Carboxylic acids; production from alcohols, page 182, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Carboxylic acids; properties and reactions of, page 184, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945725/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945725&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=694be7494de75af3349537d34e13f7f0 ''Carboxylic acids, pages 100, 102, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Carboxylic acids, pages 182-183, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948147/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948147&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f63dcd8345f4e49c717b39a228a36c7c ''Carboxylic acids, pages 305, 306, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359829/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359829&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=90e8d7b4f039d53035238fa0320fe00b ''Carboxylic acids, pages 236-237, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945679/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945679&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a2db42f7b4bdf10cafaafa3bb9120940 ''Carboxylic acids, pages 89, 91, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR Gateway ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:06, 1 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Carboxylic Acids are organic compounds with a Carbon atom which has a double bonds to an Oxygen atom and a single bond to an OH group. The general formula is CnH2nO2.
About Carboxylic Acids
- Carboxylic Acids are a homologous series of organic compounds.
- The functional group of the Carboxylic Acids is the double bond between a Carbon atom and an Oxygen atom and the single bond to an OH group.
- Carboxylic Acids are long chains of Carbon atoms covalently bonded together with the the final Carbon atom in the chain as a COOH group.
Examples
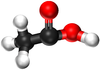
Methanoic Acid
ReferencesAQA
|
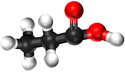
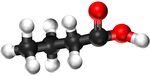
Ethanoic Acid | Propanoic Acid | Butanoic Acid | |
| Chemical Formula | CH2O2 | C2H4O2 | C3H6O2 | C4H8O2 |
| Structural Formula | HCOOH | CH3COOH | CH3CH2COOH | CH3CH2CH2COOH |
| Structural Diagram | ||||
| Ball and Stick Model |
Reactions of Carboxylic Acids
Neutralisation
Carboxylic Acids can be neutralised to produce organic salts.
\(2HCOOH + 2K → 2HCOOK + H_2\)
\(2CH_3COOH + MgO → (CH3COO)_2Mg + H_2O\)
\(C_2H_5COOH + NaOH → C_2H_5COONa + H_2O\)
\(2C_3H_7COOH + MgCO_3 → (C_3H_7COO)_2Mg + H_2O + CO_2\)
Esterification
Carboxylic Acids may react with alcohols to produce compounds known as esters which have the functional group -COO-.
- Methanoic Acid + Ethanol → Ethyl Methanoate + Water
\(HCOOH + C2_H_5OH → HCOOC_2H_5 + H_2O\)
- Ethanoic Acid + Ethanol → Ethyl Ethanoate + Water
\(CH_3COOH + C_2H_5OH → CH_3COOC_2H_5 + H_2O\)
- Propanoic Acid + Propanol → Propyl Propanoate + Water
\(C_3H_5COOH + C_3H_7OH → C_2H_5COOC_3H_7 + H_2O\)
- Butanoic Acid + Propanol → Propyl Butanoate + Water
\(C_3H_5COOH + C_3H_7OH → C_3H_5COOC_3H_7 + H_2O\)
References
AQA
- Carboxylic acids, page 183, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Carboxylic acids, page 82, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Carboxylic acids, pages 161, 163-165, 170-171, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Carboxylic acids, pages 242, 243, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Carboxylic acids; production from alcohols, page 182, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Carboxylic acids; properties and reactions of, page 184, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Carboxylic acids, pages 100, 102, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Carboxylic acids, pages 182-183, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Carboxylic acids, pages 305, 306, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel