Difference between revisions of "Giant Ionic Structure"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 4== ===Meaning=== '''Giant ionic structures''' are large molecules in which the atoms are held together by ionic bonds. ===About Giant Ioni...") |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
|[[File:GiantIonicSodiumChloride.png|center|400px]] | |[[File:GiantIonicSodiumChloride.png|center|400px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
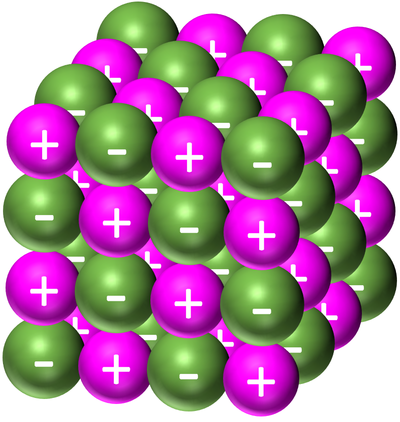
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Sodium Chloride]] forms a '''giant ionic structure'''. The [[Sodium]] is represented by the light | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Sodium Chloride]] forms a '''giant ionic structure'''. The [[Sodium]] is represented by the light purple [[Positive Ion|positive ion]]s and the [[Chloride]] is represented by the green [[Negative Ion|negative ions]]. |
|} | |} | ||
===Bulk Properties=== | ===Bulk Properties=== | ||
| + | : '''Giant ionic structures''' are poor [[Electrical Conductor|electrical conductors]] because the [[ion]]s are not free to move. | ||
| + | : Most '''giant ionic structures''' can be broken down and [[dissolve]]d in [[water]]. | ||
| + | : [[Giant Ionic Structure|Giant ionic structures]] have high [[Melting Point|melting points]] due to the strong [[Electrostatic Force|electrostatic force]] between the [[ion]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Giant ionic structures, pages 42-43, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:30, 5 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Giant ionic structures are large molecules in which the atoms are held together by ionic bonds.
About Giant Ionic Structures
- Giant ionic structures are molecules made of a large number of metal and non-metal ions joined by ionic bonds.
- The ions in a giant ionic structure are arranged in a regular lattice (a repeating pattern of elements.
Examples
| Sodium Chloride forms a giant ionic structure. The Sodium is represented by the light purple positive ions and the Chloride is represented by the green negative ions. |
Bulk Properties
- Giant ionic structures are poor electrical conductors because the ions are not free to move.
- Most giant ionic structures can be broken down and dissolved in water.
- Giant ionic structures have high melting points due to the strong electrostatic force between the ions.