Difference between revisions of "Mirror"
(→About Mirrors) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Key Stage 2== | ==Key Stage 2== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | [[File:WingMirror.png|right|300px|thumb|A picture showing the wing mirror of a car.]] | ||
A '''mirror''' is a shiny surface used to [[Reflection|reflect]] the image of an object. | A '''mirror''' is a shiny surface used to [[Reflection|reflect]] the image of an object. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 28: | ||
: A [[mirror]] can be used to change the direction of [[light]] by [[Reflection|reflecting]] it. | : A [[mirror]] can be used to change the direction of [[light]] by [[Reflection|reflecting]] it. | ||
: A [[mirror]] makes an [[object]] look like it's in a place that it is not. | : A [[mirror]] makes an [[object]] look like it's in a place that it is not. | ||
| − | : [[Reflection]] from a [[mirror]] follows the Law of Reflection. | + | : [[Reflection]] from a [[mirror]] follows the [[Law of Reflection]]. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 35: | Line 36: | ||
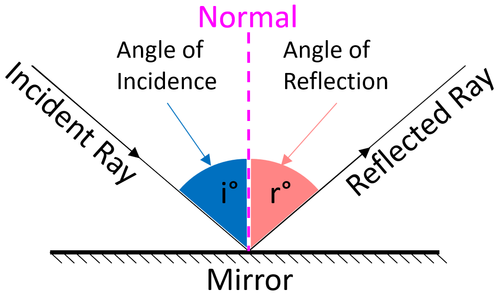
| style="height:20px; width:500px; text-align:center;" |When a [[Light Ray|ray of light]] strikes a [[mirror]] it is [[Reflection|reflected]] by the same angle that it arrives. | | style="height:20px; width:500px; text-align:center;" |When a [[Light Ray|ray of light]] strikes a [[mirror]] it is [[Reflection|reflected]] by the same angle that it arrives. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Mirrors; images in, page 189, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Mirrors; reflection of light, pages 188-9, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''Mirrors, page 189, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:10, 15 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
A mirror is a shiny surface used to reflect the image of an object.
About Mirrors
- Mirrors are usually made of metal because it is shiny. The metal is sometimes covered in glass to protect the metal.
- A mirror can be used to change the direction of light by reflecting it.
- A mirror makes an object look like it's in a place that it is not.
Examples
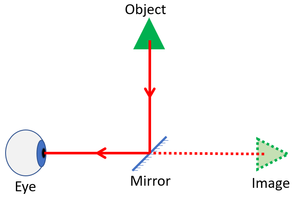
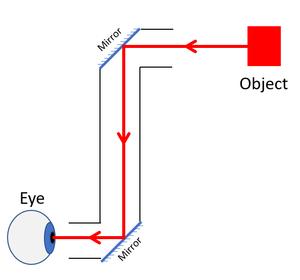
| This mirror makes it look like the triangle is in front of the eye, but it is not. | A periscope uses the reflection from two mirrors to see a clear image. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A mirror is a shiny surface used to reflect the image of an object.
About Mirrors
- Mirrors are usually made of metal because it is shiny. The metal is sometimes covered in glass to protect the metal.
- A mirror can be used to change the direction of light by reflecting it.
- A mirror makes an object look like it's in a place that it is not.
- Reflection from a mirror follows the Law of Reflection.
| When a ray of light strikes a mirror it is reflected by the same angle that it arrives. |
References
AQA
- Mirrors; images in, page 189, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Mirrors; reflection of light, pages 188-9, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA