Difference between revisions of "Smelting"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 3== ===Meaning=== Smelting is a process for extracting metals by heating and melting a mineral with carbon to cause a Di...") |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
: Any [[metal]] below [[Carbon]] on the [[Reactivity Series]] can be [[Extraction of Metals|extracted]] from its by [[smelting]] with [[Carbon]]. | : Any [[metal]] below [[Carbon]] on the [[Reactivity Series]] can be [[Extraction of Metals|extracted]] from its by [[smelting]] with [[Carbon]]. | ||
: When the [[ore]] is [[melting|melted]] it [[Carbon]] is added and a [[Displacement Reaction|displacement reaction]] happens where the [[Carbon]] replaces the [[metal]] in the [[mineral]]. | : When the [[ore]] is [[melting|melted]] it [[Carbon]] is added and a [[Displacement Reaction|displacement reaction]] happens where the [[Carbon]] replaces the [[metal]] in the [[mineral]]. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:SmeltingFurnace.png|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
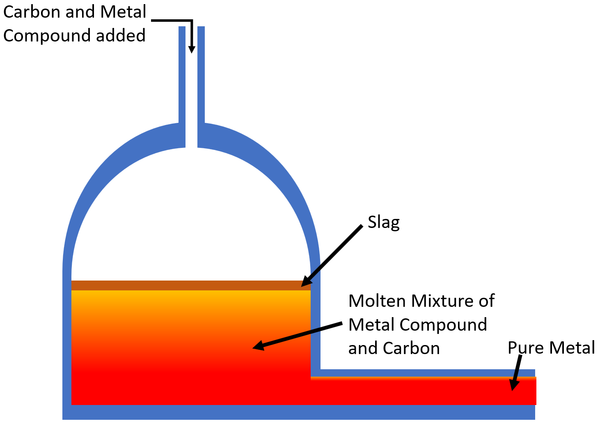
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[Carbon]] [[Chemical Reaction|reacts]] with the [[mineral]] in a [[Displacement Reaction|displacement reaction]] creating usually producing [[Carbon Dioxide]] and the [[pure]] [[metal]] which is removed from the furnace. Any [[Impurity|impurities]] in the [[mineral]] rise to the top and make a layer called slag which is removed. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Example Reactions=== | ||
| + | : Iron Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Iron | ||
| + | : Zinc Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Zinc | ||
| + | : Tin Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Tin | ||
| + | : Lead Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Lead | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | [[Smelting]] is a process for [[Extraction of Metals|extracting metals]] by heating and [[melting]] a [[mineral]] with [[carbon]] to cause a [[Displacement Reaction|displacement reaction]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Smelting=== | ||
| + | : Any [[metal]] below [[Carbon]] on the [[Reactivity Series]] can be [[Extraction of Metals|extracted]] from its by [[smelting]] with [[Carbon]]. | ||
| + | : When an [[ore]] containing a [[Metal Oxide|metal oxide]] is [[melting|melted]] [[Carbon]] is added and a [[Displacement Reaction|displacement reaction]] happens where the [[Carbon]] replaces the [[metal]] in the [[mineral]]. | ||
| + | : When an [[ore]] containing a [[Metal Carbonate|metal carbonate]] a [[Displacement Reaction|displacement reaction]] and a [[Thermal Decomposition|thermal decomposition reaction]] take place. | ||
| + | : [[Smelting]] requires a lot of [[energy]] to [[heat]] the [[mineral]] beyond its [[Melting Point|melting point]] so it can be expensive to carry out. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Example Reactions=== | ||
| + | Iron Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Iron | ||
| + | : <chem>2Fe2O3 + 3C -> 3CO2 + 4Fe</chem> | ||
| + | Zinc Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Zinc | ||
| + | : <chem>2ZnO + C -> CO2 + 2Zn</chem> | ||
| + | Tin Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Tin | ||
| + | : <chem>SnO2 + C -> CO2 + Sn</chem> | ||
| + | Lead Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Lead | ||
| + | : <Chem>2PbO + C -> CO2 + 2Pb</chem> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Zinc Carbonate + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Zinc | ||
| + | : <chem>2ZnCO3 + C -> 3CO2 + 2Zn</chem> | ||
| + | Copper Carbonate Hydroxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Copper | ||
| + | : <chem>Cu2(CO3)(OH)2 + C -> 2CO2 + H2O + 2Cu</chem> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Smelting, pages 212, 217, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:00, 13 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Smelting is a process for extracting metals by heating and melting a mineral with carbon to cause a displacement reaction.
About Smelting
- Any metal below Carbon on the Reactivity Series can be extracted from its by smelting with Carbon.
- When the ore is melted it Carbon is added and a displacement reaction happens where the Carbon replaces the metal in the mineral.
| The Carbon reacts with the mineral in a displacement reaction creating usually producing Carbon Dioxide and the pure metal which is removed from the furnace. Any impurities in the mineral rise to the top and make a layer called slag which is removed. |
Example Reactions
- Iron Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Iron
- Zinc Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Zinc
- Tin Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Tin
- Lead Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Lead
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Smelting is a process for extracting metals by heating and melting a mineral with carbon to cause a displacement reaction.
About Smelting
- Any metal below Carbon on the Reactivity Series can be extracted from its by smelting with Carbon.
- When an ore containing a metal oxide is melted Carbon is added and a displacement reaction happens where the Carbon replaces the metal in the mineral.
- When an ore containing a metal carbonate a displacement reaction and a thermal decomposition reaction take place.
- Smelting requires a lot of energy to heat the mineral beyond its melting point so it can be expensive to carry out.
Example Reactions
Iron Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Iron
- <chem>2Fe2O3 + 3C -> 3CO2 + 4Fe</chem>
Zinc Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Zinc
- <chem>2ZnO + C -> CO2 + 2Zn</chem>
Tin Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Tin
- <chem>SnO2 + C -> CO2 + Sn</chem>
Lead Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Lead
- <Chem>2PbO + C -> CO2 + 2Pb</chem>
Zinc Carbonate + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Zinc
- <chem>2ZnCO3 + C -> 3CO2 + 2Zn</chem>
Copper Carbonate Hydroxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Copper
- <chem>Cu2(CO3)(OH)2 + C -> 2CO2 + H2O + 2Cu</chem>