Difference between revisions of "Specular Reflection"
| (11 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[File: | + | |[[File:ReflectionLake.png|center|200px]] |
| + | |[[File:ReflectionGlass.png|center|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:500px; text-align:center;" | | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |You can see the '''reflection''' of the mountain and clouds on the surface of the water. |
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The glass '''reflects''' the image of the clouds. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:ReflectionGlasses.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:ReflectionEye.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |These glasses are very '''reflective'''. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |You can sometimes see a '''reflection''' is a person's eye. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | [[Specular Reflection]] is when [[light]] bounces off a flat surface to produce a an [[image]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Specular Reflection=== | ||
| + | : [[Specular Reflection]] happens from a shiny surface and makes an [[image]] (you can see a 'reflection'). | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:SpecularReflectionDiagram.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
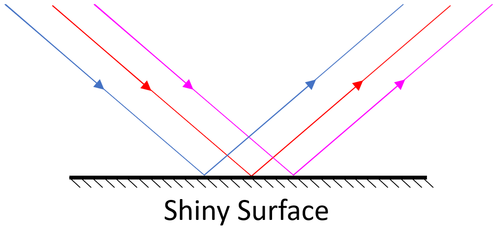
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Specular Reflection]] happens from a smooth surface. Parallel rays are '''reflected''' and stay parallel to one another. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===The Law of Reflection=== | ||
| + | : The Law of '''reflection''' states that the [[Angle of Incidence|angle of incidence]] is equal to the [[Angle of Reflection|angle of reflection]]. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:ReflectionDiagram.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Specular Reflection]] from the [[glass]] makes an [[image]] of the sky in the [[glass]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | [[Specular Reflection]] is when an [[Electromagnetic Wave]] bounces off the [[interface]] between a [[transparent]] [[medium]] and an [[opaque]] [[medium]] with a flat surface to produce an [[image]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Specular Reflection=== | ||
| + | : [[Specular Reflection]] happens from a shiny surface and makes an [[image]] (you can see a 'reflection'). | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:SpecularReflectionDiagram.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Specular Reflection]] happens from a smooth surface. Parallel rays are '''reflected''' and stay parallel to one another. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===The Law of Reflection=== | ||
| + | : The Law of '''reflection''' states that the [[Angle of Incidence|angle of incidence]] is equal to the [[Angle of Reflection|angle of reflection]]. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:ReflectionDiagram.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
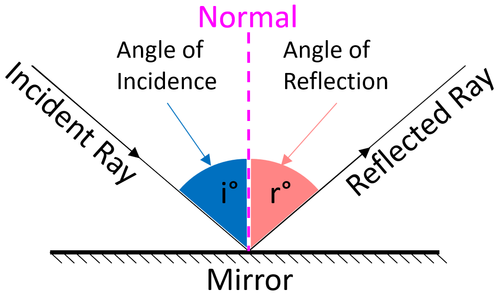
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[angle]] between the [[Incident Ray|incident ray]] and the [[normal]] ([[Angle of Incidence|angle of incidence]]) is the same as the [[angle]] between the [[Reflected Ray|reflected ray]] and the [[normal]] ([[Angle of Reflection|angle of reflection]]). | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Specular reflection, page 203, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Specular reflection, page 208, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Specular reflection, page 235, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac420 ''Specular reflection, pages 75, 77, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Specular reflection, page 115, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945733/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945733&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=2a2dbec9db6bf5766c0458d908fa0a52 ''Specular reflection, page 38, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120223/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120223&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=068ecf40278c32406a7f1c6e66751417 ''Specular reflection, page 68, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Specular reflection, pages 165, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:57, 20 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning

A mirror reflects light so we can see a perfect image.
Reflection from shiny surfaces is when light bounces off a material creating an image that we can see.
About Reflection form Shiny Surfaces
- When a surface is shiny we can see a reflection on the surface.
- A mirror is a shiny piece of metal that reflects all of the light that hits it and allows us to see an image.
- Mirrors are said to be reflective.
- If a surface is dull you cannot see an image and it is not called reflective, but it still reflects the light.
| You can see the reflection of the mountain and clouds on the surface of the water. | The glass reflects the image of the clouds. |
| These glasses are very reflective. | You can sometimes see a reflection is a person's eye. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Specular Reflection is when light bounces off a flat surface to produce a an image.
About Specular Reflection
- Specular Reflection happens from a shiny surface and makes an image (you can see a 'reflection').
| Specular Reflection happens from a smooth surface. Parallel rays are reflected and stay parallel to one another. |
The Law of Reflection
- The Law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
| Specular Reflection from the glass makes an image of the sky in the glass. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Specular Reflection is when an Electromagnetic Wave bounces off the interface between a transparent medium and an opaque medium with a flat surface to produce an image.
About Specular Reflection
- Specular Reflection happens from a shiny surface and makes an image (you can see a 'reflection').
| Specular Reflection happens from a smooth surface. Parallel rays are reflected and stay parallel to one another. |
The Law of Reflection
- The Law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
| The angle between the incident ray and the normal (angle of incidence) is the same as the angle between the reflected ray and the normal (angle of reflection). |
References
AQA
- Specular reflection, page 203, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Specular reflection, page 208, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Specular reflection, page 235, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Specular reflection, pages 75, 77, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Specular reflection, page 115, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Specular reflection, page 38, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Specular reflection, page 68, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel