Difference between revisions of "Photon"
(→The Speed of Light) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
===About Photons=== | ===About Photons=== | ||
: The '''photon''' is denoted with the lower case Greek letter <math>\gamma</math> (gamma). | : The '''photon''' is denoted with the lower case Greek letter <math>\gamma</math> (gamma). | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
: '''Photons''' carry [[energy]] from one place to another. | : '''Photons''' carry [[energy]] from one place to another. | ||
| + | : '''Photons''' have no [[mass]] or [[Electrical Charge|charge]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Virtual Photons=== | ||
| + | : '''Virtual photons''' a [[model]] for the mechanism of action of the [[Electromagnetic Interaction|electromagnetic interaction]], but they are not strictly 'real'. | ||
| + | : '''Virtual photons''' have no [[mass]] and therefore can mediate the [[Electromagnetic Interaction|electromagnetic interaction]] over an infinite range. | ||
| + | : '''Virtual photons''' carry [[momentum]] without carrying [[mass]] and are therefore able to change the direction of motion of other [[Subatomic Particle|subatomic particles]]. | ||
| + | : '''Virtual photons''' do not carry [[Electrical Charge|charge]], but allow [[Subatomic Particle|particles]] with [[Electrical Charge|charge]] to exchange [[momentum]]. | ||
===Equations=== | ===Equations=== | ||
| Line 37: | Line 41: | ||
====The Speed of Light==== | ====The Speed of Light==== | ||
| − | <math> | + | <math>c = f\lambda</math> |
Where | Where | ||
| Line 46: | Line 50: | ||
<math>f =</math> The [[frequency]] of the [[Electromagnetic Wave|wave]] associated with the '''photon'''. | <math>f =</math> The [[frequency]] of the [[Electromagnetic Wave|wave]] associated with the '''photon'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Examples=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+The '''virtual photon''' is shown mediating the [[Electromagnetic Interaction|electromagnetic interaction]]. | ||
| + | |[[File:FeynmanDiagramProtonProton.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:FeynmanDiagramElectronElectron.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
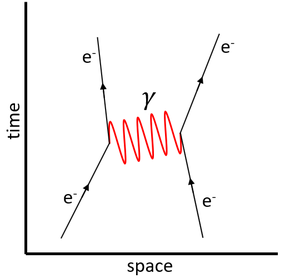
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |This [[Feynman Diagram]] shows the [[Electromagnetic Interaction|electromagnetic interaction]] between two [[proton]]s exchanging [[momentum]] via the '''virtual photon'''. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |This [[Feynman Diagram]] shows the [[Electromagnetic Interaction|electromagnetic interaction]] between two [[electron]]s exchanging [[momentum]] via the '''virtual photon'''. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Photons, page 95, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Photons, pages 178-179, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:16, 17 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 5
Meaning
Photons (\(\gamma\)) are bosons responsible for mediating the electromagnetic interaction and are the particle associated with electromagnetic waves.
About Photons
- The photon is denoted with the lower case Greek letter \(\gamma\) (gamma).
- Photons carry energy from one place to another.
- Photons have no mass or charge
About Virtual Photons
- Virtual photons a model for the mechanism of action of the electromagnetic interaction, but they are not strictly 'real'.
- Virtual photons have no mass and therefore can mediate the electromagnetic interaction over an infinite range.
- Virtual photons carry momentum without carrying mass and are therefore able to change the direction of motion of other subatomic particles.
- Virtual photons do not carry charge, but allow particles with charge to exchange momentum.
Equations
Momentum of a Photon
\(p = \frac{h}{\lambda}\)
Where
\(p =\) The momentum of the photon.
\(h = \) Planck's Constant (\(6.63\times10^{-34}Js\)).
\(\lambda =\) The wavelength of the wave associated with the photon.
Energy of a Photon
\(E = hf\)
Where
\(E =\) The energy of the photon.
\(h = \) Planck's Constant (\(6.63\times10^{-34}Js\)).
\(f =\) The frequency of the wave associated with the photon.
The Speed of Light
\(c = f\lambda\)
Where
\(c =\) The speed of light (\(3.00\times10^{8}ms^{-1}\) in a vacuum).
\(\lambda =\) The wavelength of the wave associated with the photon.
\(f =\) The frequency of the wave associated with the photon.
Examples
| This Feynman Diagram shows the electromagnetic interaction between two protons exchanging momentum via the virtual photon. | This Feynman Diagram shows the electromagnetic interaction between two electrons exchanging momentum via the virtual photon. |