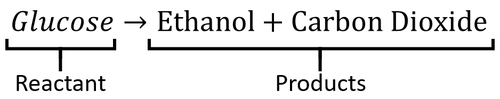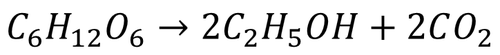Difference between revisions of "Fermentation"
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
===About Fermentation=== | ===About Fermentation=== | ||
| − | : [[Fermentation]] | + | : [[Fermentation]] generally uses yeast or [[bacteria]] which may [[Aerobic Respiration|aerobically]] or [[Anaerobic Respiration|anaerobically respire]] in our food. |
| − | : [[Fermentation]] is | + | : Humans use [[fermentation]] to change the flavour of food or release some of the [[nutrient]]s that otherwise could not be [[digestion|digested]]. |
| + | Some common food and drinks that are '''fermented''' | ||
| + | *Bread | ||
| + | *Yoghurt | ||
| + | *Sauerkraut | ||
| + | *[[Alcohol (Drug)|Alcohol]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Word Equation for Fermentation by Yeast=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:FermentationWordEquation.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:500px; text-align:center;" |The word equation for '''fermentation''' in [[yeast]] showing the [[reactant]]s and [[product]]s. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Symbol Equation for Fermentation by Yeast=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:FermentationBalancedSymbolEquation.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:500px; text-align:center;" |The balanced symbol equation for '''fermentation''' by [[yeast]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Extra Information=== | ||
| + | {{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eksagPy5tmQ}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | [[Fermentation]] is a process in which [[micro-organism]]s are allowed to consume the [[sugar]] in a food in order to change the flavour or create a new [[chemical]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359373/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359373&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=952a73bbb09d222ecc4b50d200679849 ''Fermentation, page 139, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Fermentation, page 162, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=5ec5fc3f6429e30c1d9ab9bca2bccf93 ''Fermentation, page 162, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945954/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945954&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=100574c08fbbb64318256eb79ed61a76 ''Fermentation, page 176, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158762/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158762&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a0fffa35b3ea49a63404f6704e0df7cc ''Fermentation, page 242-3, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945563/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945563&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9a1d023a374038e6072f33c4f3cf808b ''Fermentation, page 62, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945571/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945571&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9e29fad914244909903e5e93f8a01d123 ''Fermentation, page 81, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''Fermentation, pages 109-10, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158754/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158754&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=27ad53b0283feeff7fc5ae04a9e205f292 ''Fermentation, pages 13, 38-39, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Fermentation, pages 240, 241, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Fermentation, pages 176-177, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948147/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948147&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f63dcd8345f4e49c717b39a228a36c7c ''Fermentation, pages 301, 302, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945725/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945725&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=694be7494de75af3349537d34e13f7f0 ''Fermentation, pages 82, 103, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359810/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359810&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=d768d99f1a06f7c12fab40e5aef85a55 ''Fermentation, page 43, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359829/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359829&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=90e8d7b4f039d53035238fa0320fe00b ''Fermentation, pages 204, 205, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:58, 7 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Fermentation is a process in which micro-organisms are allowed to consume the sugar in a food in order to change the flavour or create a new chemical.
About Fermentation
- Fermentation generally uses yeast or bacteria which may aerobically or anaerobically respire in our food.
- Humans use fermentation to change the flavour of food or release some of the nutrients that otherwise could not be digested.
Some common food and drinks that are fermented
- Bread
- Yoghurt
- Sauerkraut
- Alcohol
Word Equation for Fermentation by Yeast
| The word equation for fermentation in yeast showing the reactants and products. |
Symbol Equation for Fermentation by Yeast
| The balanced symbol equation for fermentation by yeast. |
Extra Information
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Fermentation is a process in which micro-organisms are allowed to consume the sugar in a food in order to change the flavour or create a new chemical.
References
AQA
- Fermentation, page 139, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Fermentation, page 162, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Fermentation, page 162, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Fermentation, page 176, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Fermentation, page 242-3, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Fermentation, page 62, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Fermentation, page 81, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Fermentation, pages 109-10, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Fermentation, pages 13, 38-39, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Fermentation, pages 240, 241, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Fermentation, pages 176-177, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Fermentation, pages 301, 302, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Fermentation, pages 82, 103, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel