Difference between revisions of "Angle of Refraction"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 3== ===Meaning=== The '''angle of refraction''' is the angle between the between the refracted ray and the normal. ===Examples=== {| cla...") |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
The '''angle of refraction''' is the [[angle]] between the between the [[Refracted Ray|refracted ray]] and the [[normal]]. | The '''angle of refraction''' is the [[angle]] between the between the [[Refracted Ray|refracted ray]] and the [[normal]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About the Angle of Refraction=== | ||
| + | : When [[light]] travels from [[air]] into [[glass]] the '''angle of refraction''' is always smaller than the [[Angle of Incidence|angle of incidence]]. | ||
| + | : When [[light]] travels from [[glass]] into [[air]] the '''angle of refraction''' is always greater than the [[Angle of Incidence|angle of incidence]]. | ||
===Examples=== | ===Examples=== | ||
| Line 8: | Line 12: | ||
|[[File:RefractionGlassBlock.png|center|600px]] | |[[File:RefractionGlassBlock.png|center|600px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;"|The '''angle of incidence''' is highlighted in | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;"|The '''angle of incidence''' is highlighted in pale red in this [[diagram]]. |
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4 Higher== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | The '''angle of refraction''' is the [[angle]] between the between the [[Refracted Ray|refracted ray]] and the [[normal]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About the Angle of Refraction=== | ||
| + | : When [[light]] travels from a less [[Optical Density|optically dense]] [[medium]] (such as [[air]] to a more [[Optical Density|optically dense]] [[medium]] (such as [[glass]] or [[water]] the '''angle of refraction''' is always smaller than the [[Angle of Incidence|angle of incidence]]. | ||
| + | : When [[light]] travels from a more [[Optical Density|optically dense]] [[medium]] (such as [[glass]] or [[water]]) into a less [[Optical Density|optically dense]] [[medium]] (such as [[air]]) the '''angle of refraction''' is always greater than the [[Angle of Incidence|angle of incidence]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Examples=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:RefractionGlassBlock.png|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;"|The '''angle of incidence''' is highlighted in pale red in this [[diagram]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Angle of refraction, page 195, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA'] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Angle of refraction, pages 195-197, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA'] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Angle of refraction, pages 232-234, 237, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA'] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac19 ''Angle of refraction, pages 76, 77, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA'] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Angle; of refraction, pages 203, 205, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA'] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe09680 ''Angles; of refraction, page 222, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA'] | ||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Angles; of refraction, page 99, 100, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:23, 29 October 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
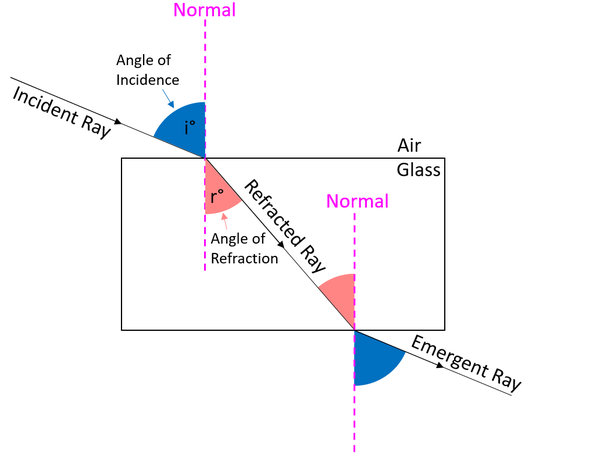
The angle of refraction is the angle between the between the refracted ray and the normal.
About the Angle of Refraction
- When light travels from air into glass the angle of refraction is always smaller than the angle of incidence.
- When light travels from glass into air the angle of refraction is always greater than the angle of incidence.
Examples
| The angle of incidence is highlighted in pale red in this diagram. |
Key Stage 4 Higher
Meaning
The angle of refraction is the angle between the between the refracted ray and the normal.
About the Angle of Refraction
- When light travels from a less optically dense medium (such as air to a more optically dense medium (such as glass or water the angle of refraction is always smaller than the angle of incidence.
- When light travels from a more optically dense medium (such as glass or water) into a less optically dense medium (such as air) the angle of refraction is always greater than the angle of incidence.
Examples
| The angle of incidence is highlighted in pale red in this diagram. |
References
AQA
- Angle of refraction, page 195, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA'
- Angle of refraction, pages 195-197, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA'
- Angle of refraction, pages 232-234, 237, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA'
- Angle of refraction, pages 76, 77, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA'
- Angle; of refraction, pages 203, 205, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA'
- Angles; of refraction, page 222, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA'