Difference between revisions of "Generator Effect"
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
: The '''generator effect''' is used in [[Power Station|power stations]] to generate [[electricity]]. | : The '''generator effect''' is used in [[Power Station|power stations]] to generate [[electricity]]. | ||
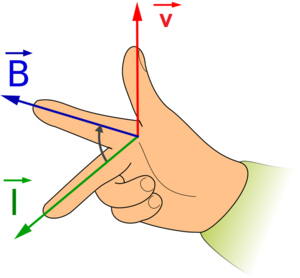
: The direction of the [[Electrical Current|current]] induced is shown by the 'right hand generator rule'. | : The direction of the [[Electrical Current|current]] induced is shown by the 'right hand generator rule'. | ||
| + | : The '''generator effect''' is used in [[alternator]]s and [[dynamo]]s. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:RightHandGeneratorRule.png|center|300px]] | ||
|[[File:GeneratorEffect.png|center|300px]] | |[[File:GeneratorEffect.png|center|300px]] | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" | | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" | | ||
| Line 19: | Line 20: | ||
<math>\overrightarrow{I}</math>: Second finger [[Electrical Current|current]]. | <math>\overrightarrow{I}</math>: Second finger [[Electrical Current|current]]. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[diagram]] shows that as the [[wire]] is moved through the [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]] a [[Electrical Current|current]] can be '''generated'''. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| − | + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Generator effect, page 232, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | |
| − | + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Generator effect, pages 222-225, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | |
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Generator effect, pages 258, 261-3, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Generator effect, pages 303-306, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac218 ''Generator effect, pages 96, 97, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Generator effect; in microphones, page 307, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Generator effect; in transformers, pages 308, 309, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Generator effect; uses of, pages 234-5, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:14, 5 November 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
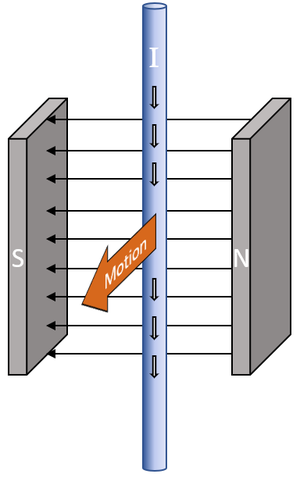
The generator effect is the current induced in a wire when it is in the region of a changing magnetic field.
About The Generator Effect
- When a wire is moved through a magnetic field at right angles to the field lines it causes a potential difference across the wire. If that wire is part of a circuit this will induce a current.
- The generator effect takes place whenever a wire is in a changing magnetic field. This change can be due to the relative motion of the wire and magnet or by the magnetic field changing over time.
- The generator effect is used in power stations to generate electricity.
- The direction of the current induced is shown by the 'right hand generator rule'.
- The generator effect is used in alternators and dynamos.
|
\(\overrightarrow{B}\): First finger field. \(\overrightarrow{v}\): The motion of the wire. \(\overrightarrow{I}\): Second finger current. |
This diagram shows that as the wire is moved through the magnetic field a current can be generated. |
References
AQA
- Generator effect, page 232, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Generator effect, pages 222-225, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Generator effect, pages 258, 261-3, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Generator effect, pages 303-306, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Generator effect, pages 96, 97, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Generator effect; in microphones, page 307, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Generator effect; in transformers, pages 308, 309, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Generator effect; uses of, pages 234-5, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA