Difference between revisions of "Resultant Force"
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
: The '''resultant force''' is 2[[N]] to the left. | : The '''resultant force''' is 2[[N]] to the left. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | The '''resultant force''' is the [[sum]] of all [[force]]s acting on an [[object]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Resultant Forces=== | ||
| + | : When [[force]]s act in the same direction their [[magnitude]]s are added together. | ||
| + | : When [[force]]s act along the same line but in opposite directions; one is [[Subtraction|subtracted]] from the other. | ||
Revision as of 12:46, 5 February 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
The Resultant Force is the overall force on an object.
About Resultant Forces
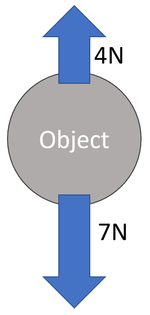
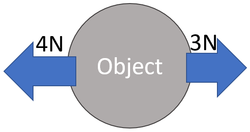
- A resultant force can be calculated by taking forces that act in opposite directions and subtracting one from the other.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The resultant force is the sum of all forces acting on an object.
About Resultant Forces
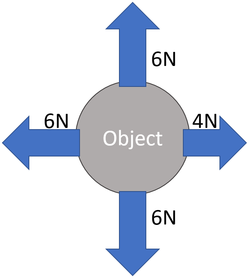
- When forces act in the same direction their magnitudes are added together.
- When forces act along the same line but in opposite directions; one is subtracted from the other.